Abstract
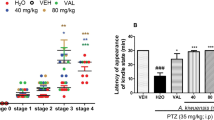
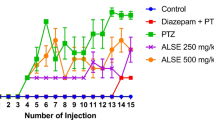
A substantial number of epileptic patients are resistant to the current medication thus necessitating the search for alternative therapies for intractable forms of the disease. Previous studies demonstrated the acute anticonvulsant properties of the methanol extract of the stem bark of Psychotria camptopus (MEPC) in rats. This study investigated the effects of MEPC on pentylenetetrazole-kindled Wistar rats. Kindling was induced by intraperitoneal injection of pentylenetetrazole (37.5 mg/kg) on every alternate day, 1 h after each daily oral pretreatment of rats (8 ≤ n ≤ 10) with MEPC (40, 80 and 120 mg/kg), vehicle or diazepam (3 mg/kg) for 43 days. The kindling development was monitored based on seizure episodes and severity. Rats’ brains were collected on day 43 for the determination of oxidative stress parameters. The histomorphological features and neuronal cell viability of the prefrontal cortex (PFC) and hippocampus were also assessed using H&E and Cresyl violet stains. Chronic administration of pentylenetetrazole time-dependently decreased the latency to myoclonic and generalized seizures, and increased seizure scores and the number of kindled rats. MEPC and diazepam significantly increased the latencies to myoclonic jerks and generalized tonic-clonic seizures. These substances also reduced seizure score and the number of rats with PTZ-kindling. MEPC improved glutathione status and decreased lipid peroxidation in the brains of kindled rats. MEPC also exhibited neuroprotection against pentylenetetrazole-induced hippocampal and PFC neuronal damages. These results suggest that P. camptopus has antiepileptogenic activity, which might be related to the augmentation of antioxidant and neuroprotective defense mechanisms, and further confirm its usefulness in the management of epilepsy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MEPC:
-
Methanol extract of the stem bark of Psychotria camptopus
- PFC:
-
prefrontal cortex
- ROS:
-
reactive oxygen species
- RNS:
-
reactive nitrogen species
- PTZ:
-
pentylenetetrazole
- TLE:
-
temporal lobe epilepsy
- NBF:
-
neutral buffer formalin
- MDA:
-
malondialdehyde
- GSH:
-
glutathione
- SOD:
-
superoxide dismutase
- CAT:
-
catalase
References
Abdel-Zaher AO, Farghaly HSM, Farrag MMY et al (2017) A potential mechanism for the ameliorative effect of thymoquinone on pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling and cognitive impairments in mice. Biomed Pharmacother 88:553–561. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biopha.2017.01.009
Aldawsari HM, Eid BG, Neamatallah T et al (2017) Anticonvulsant and Neuroprotective Activities of Phragmanthera austroarabica Extract in Pentylenetetrazole-Kindled Mice Evidence-based. Complement Altern Med:2017. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/5148219
Ashrafi MR, Shams S, Nouri M et al (2007) A probable causative factor for an old problem: selenium and glutathione peroxidase appear to play important roles in epilepsy pathogenesis. Epilepsia 48:1750–1755. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1528-1167.2007.01143.x
Bascuñana P, Javela J, Delgado M et al (2016) [18F]FDG PET neuroimaging predicts Pentylenetetrazole (PTZ) kindling outcome in rats. Mol Imaging Biol 18:733–740. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11307-016-0950-0
Clark JD, Gebhart GF, Gonder JC et al (1997) The 1996 guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. ILAR J 38:41–48. https://doi.org/10.1093/ilar.38.1.41
Corda MG, Orlandi M, Lecca D et al (1991) Pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling in rats: effect of GABA function inhibitors. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 40:329–333. https://doi.org/10.1016/0091-3057(91)90562-G
Dariani S, Baluchnejadmojarad T, Roghani M (2013) Thymoquinone attenuates astrogliosis, neurodegeneration, mossy fiber sprouting, and oxidative stress in a model of temporal lobe epilepsy. J Mol Neurosci 51:679–686. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12031-013-0043-3
Davoudi M, Shojaei A, Palizvan MR et al (2013) Comparison between standard protocol and a novel window protocol for induction of pentylenetetrazol kindled seizures in the rat. Epilepsy Res 106:54–63. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2013.03.016
De Luca G, Di Giorgio RM, Macaione S et al (2005) Amino acid levels in some lethargic mouse brain areas before and after pentylenetetrazole kindling. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 81:47–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2005.02.012
Devinsky O, Vezzani A, O’Brien TJ et al (2018) Epilepsy. Nat Rev Dis Prim 3:1–24. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2018.24
Dhir A (2012) Pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) kindling model of epilepsy. Curr Protoc Neurosci 1:1–12. https://doi.org/10.1002/0471142301.ns0937s58
Erkec EO (2015) Pentylenetetrazol Kindling Epilepsy Model. J Turkish Epilepsi Soc 21:6–12. https://doi.org/10.5505/epilepsi.2015.08108
Erkec OE, Arihan O, Kara M et al (2018) Effects of Leontice leontopetalum and Bongardia chrysogonum on oxidative stress and neuroprotection in PTZ kindling epilepsy in rats. Cell Mol Biol 64:71–77. https://doi.org/10.1079/9780851990804.0013
Fisher RS, Cross JH, French JA et al (2017) Operational classification of seizure types by the international league against epilepsy: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 58:522–530. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13670
Focho DA, Ndam WT, Fonge BA (2009) Medicinal plants of Aguambu - Bamumbu in the Lebialem highlands, southwest province of Cameroon. African J Pharm Pharmacol 3:001–013
Fokoua AR, Ndjenda MK, Kaptué Wuyt A et al (2021) Anticonvulsant effects of the aqueous and methanol extracts from the stem bark of Psychotria camptopus Verdc. (Rubiacaea) in rats. J Ethnopharmacol 272:113955. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2021.113955
Geronzi U, Lotti F, Grosso S (2018) Oxidative stress in epilepsy. Expert Rev Neurother 18:427–434. https://doi.org/10.1080/14737175.2018.1465410
Góth L (1991) A simple method for determination of serum catalase activity and revision of reference range. Clin Chim Acta 196:143–151. https://doi.org/10.1016/0009-8981(91)90067-M
Green MF, Kern RS, Braff DL, Mintz J (2000) Neurocognitive deficits and functional outcome in schizophrenia: are we measuring the “right stuff”? Schizophr Bull 26:119–136
Ilhan A, Gurel A, Armutcu F et al (2005) Antiepileptogenic and antioxidant effects of Nigella sativa oil against pentylenetetrazol-induced kindling in mice. Neuropharmacology 49:456–464. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuropharm.2005.04.004
Jollow D, Mitchell JR, Zampaglione N, Gillette JR (1974) Bromobenzene-induced liver necrosis. Protective role of glutathione and evidence for 3,4-bromobenzene oxide as the hepatotoxic metabolite. Pharmacology 11:151–169. https://doi.org/10.1159/000136485
Kola PK, Akula A, NissankaraRao LS, Danduga RCSR (2017) Protective effect of naringin on pentylenetetrazole (PTZ)-induced kindling; possible mechanisms of antikindling, memory improvement, and neuroprotection. Epilepsy Behav 75:114–126. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2017.07.011
Kubova H (2016a) Side effects of antiepileptic drugs. In: Talevi a, Rocha L (eds) antiepileptic drug discovery., methods in. Humana press, New York, New York, NY, pp 329–250
Kubova H (2016b) Chapter 17 side effects of antiepileptic drugs. doi: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4939-6355-3
Kumar M, Kumar P (2017) Protective effect of spermine against pentylenetetrazole kindling epilepsy induced comorbidities in mice. Neurosci Res 120:8–17. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neures.2017.02.003
Lin X, Cui Y, Wang L, Chen W (2019) Chronic exercise buffers the cognitive dysfunction and decreases the susceptibility to seizures in PTZ-treated rats. Epilepsy Behav 98:173–187. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2019.07.032
Moto FCO, Arsa’a A, Ngoupaye GT et al (2018) Anxiolytic and antiepileptic properties of the aqueous extract of Cissus quadrangularis (Vitaceae) in mice pilocarpine model of epilepsy. Front Pharmacol 9:1–10. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00751
Muke S, Kaikini A, Peshattiwar V et al (2018) Neuroprotective effect of coumarin nasal formulation: kindling model assessment of epilepsy. Front Pharmacol 9:1–16. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2018.00992
Nigar S, Pottoo F, Tabassum N et al (2016) Molecular insights into the role of inflammation and oxidative stress in epilepsy. J Adv Med Pharm Sci 10:1–9. https://doi.org/10.9734/jamps/2016/24441
Olugbemide AS, Ben-Azu B, Bakre AG et al (2021) Naringenin improves depressive- and anxiety-like behaviors in mice exposed to repeated hypoxic stress through modulation of oxido-inflammatory mediators and NF-kB/BDNF expressions. Brain Res Bull 169:214–227. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2020.12.003
Pearson-Smith JN, Patel M (2017) Metabolic dysfunction and oxidative stress in epilepsy. Int J Mol Sci 18:1–13. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms18112365
Pitkänen A, Lukasiuk K, Dudek FE, Staley KJ (2015) Epileptogenesis. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Med 5:1–18. https://doi.org/10.1101/cshperspect.a022822
Rana A, Musto AE (2018) The role of inflammation in the development of epilepsy. J Neuroinflammation 15:1–12
Ravizza T, Balosso S, Marchi N (2017) Experimental models of inflammation in epilepsy research. In: Models of seizures and epilepsy, Second edn. Elsevier Inc., Second Edi, pp 961–974
Righes Marafiga J, Vendramin Pasquetti M, Calcagnotto ME (2020) GABAergic interneurons in epilepsy: more than a simple change in inhibition. Epilepsy Behav
Roganovic M, Pantovic S, Dizdarevic S (2019) Role of the oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of epilepsy. Neurol Sci Neurophysiol 36:1–8. https://doi.org/10.5152/NSN.2019.11632
Saletti PG, Ali I, Casillas-Espinosa PM et al (2019) In search of antiepileptogenic treatments for post-traumatic epilepsy. Neurobiol Dis 123:86–99
Samokhina E, Samokhin A (2018) Neuropathological profile of the pentylenetetrazol (PTZ) kindling model. Int J Neurosci 128:1086–1096. https://doi.org/10.1080/00207454.2018.1481064
Scheffer IE, Berkovic S, Capovilla G et al (2017) ILAE classification of the epilepsies: position paper of the ILAE Commission for Classification and Terminology. Epilepsia 58:512–521. https://doi.org/10.1111/epi.13709
Shimada T, Yamagata K (2018) Pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling mouse model. J Vis Exp 2018:e56573. https://doi.org/10.3791/56573
Singh D, Goel RK (2016) Anticonvulsant mechanism of saponins fraction from adventitious roots of Ficus religiosa: possible modulation of GABAergic, calcium and sodium channel functions. Rev Bras Farmacogn 26:579–585. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bjp.2015.10.007
Singh N, Saha L, Kumari P et al (2019) Effect of dimethyl fumarate on neuroinflammation and apoptosis in pentylenetetrazol kindling model in rats. Brain Res Bull 144:233–245. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.brainresbull.2018.11.013
Singh N, Vijayanti S, Saha L et al (2018) Neuroprotective effect of Nrf2 activator dimethyl fumarate, on the hippocampal neurons in chemical kindling model in rat. Epilepsy Res 143:98–104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2018.02.011
Snehunsu A, Ghosal C, Kandwal M et al (2015) 1-Triacontanol cerotate; isolated from Marsilea quadrifolia Linn. Ameliorates reactive oxidative damage in the frontal cortex and hippocampus of chronic epileptic rats. J Ethnopharmacol 172:80–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.06.020
Sünnetçi E, Solmaz V, Erbaş O (2021) Chronic oxytocin treatment has long lasting therapeutic potential in a rat model of neonatal hypercapnic-hypoxia injury, through enhanced GABAergic signaling and by reducing hippocampal gliosis with its anti-inflammatory feature. Peptides 135. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.peptides.2020.170398
Taiwe GS, Moto FCO, Ayissi ERM et al (2015) Effects of a lyophilized aqueous extract of Feretia apodanthera Del. (Rubiaceae) on pentylenetetrazole-induced kindling, oxidative stress, and cognitive impairment in mice. Epilepsy Behav 43:100–108. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.yebeh.2014.11.022
Taiwe GS, Moto FCO, Pale S et al (2016) Extracts of Feretia apodanthera Del. Demonstrated anticonvulsant activities against seizures induced by chemicals and maximal electroshock. Epilepsy Res 127:30–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2016.08.009
Tang F, Hartz AMS, Bauer B (2017) Drug-resistant epilepsy: multiple hypotheses, few answers. Front Neurol 8:1–19. https://doi.org/10.3389/fneur.2017.00301
Tseuguem PP, Nguelefack TB, Piégang BN, Mbankou Ngassam S (2019, 2019) Aqueous and methanol extracts of Paullinia pinnata (Sapindaceae) improve monosodium Urate-induced gouty arthritis in rat: analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant effects. Evidence-based Complement Altern Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/5946291
Vasil’ev DS, Tumanova NL, Lavrent’eva VV et al (2015) The ability of NMDA-type glutamate receptor blockers to prevent the development of Pentylenetetrazole kindling and morphological changes to pyramidal neurons in the mouse Hippocampus. Neurosci Behav Physiol 45:528–535. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11055-015-0106-8
Vezzani A (2014) Epilepsy and inflammation in the brain: overview and pathophysiology. Epilepsy Curr 14:3–7
Vezzani A, Balosso S, Ravizza T (2012) Inflammation and epilepsy. In: handbook of clinical neurology, 1st edn. Elsevier B.V., pp 163–175
Wahab A (2010) Difficulties in treatment and management of epilepsy and challenges in new drug development. Pharmaceuticals 3:2090–2110. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph3072090
Waldbaum S, Patel M (2010) Mitochondria, oxidative stress, and temporal lobe epilepsy. Epilepsy Res 88:23–45. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eplepsyres.2009.09.020
Zhu X, Dong J, Han B et al (2017) Neuronal nitric oxide synthase contributes to PTZ kindling-induced cognitive impairment and depressive-like behavior. Front Behav Neurosci 11:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnbeh.2017.00203
Acknowledgements
The authors are grateful to the West African Research Association (WARA) for the financial support through the WARA travel grant 2019. We thank the University of Ibadan, Oyo state, Nigeria for the facilities provided.
Data availability
All the data and material from this study are available on demand.
Funding
This work benefits from the support of the West African Research Association (WARA) through the WARA Travel Grant 2019.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
The experimental protocols were approved by the Animal Care, Use and Research Ethics Committee of the University of Ibadan (UI-ACUREC/19/00054).
Competing interests
The authors declare no competing interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
ESM 1
(PDF 2806 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fokoua, A.R., Ajayi, A.M., Ben-Azu, B. et al. The antioxidant and neuroprotective effects of the Psychotria camptopus Verd. Hook. (Rubiaceae) stem bark methanol extract contributes to its antiepileptogenic activity against pentylenetetrazol kindling in male Wistar rats. Metab Brain Dis 36, 2015–2027 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00825-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11011-021-00825-1