We live in a very peculiar world. We are surrounded by so many things; some move, and some don’t. Some are born naturally, while others are invented or constructed by us humans. When we are born, we have no sense of the world around us. However, we learn more about it as we grow older. The more we learn about it, the more we understand how intertwined our lives are with this majestic place we call home. Everything we do is directly or indirectly connected to our surroundings. From the air we breathe to the road we walk on, each element plays an important role in our lives. As children, we are taught how to differentiate and group things to be able to better understand and identify them. One such point of differentiation is whether an object or thing is living or non-living in nature. This is one of the most basic forms of differentiation we are taught. Read on further to know some names of living and non living things.
What Are Living Things?
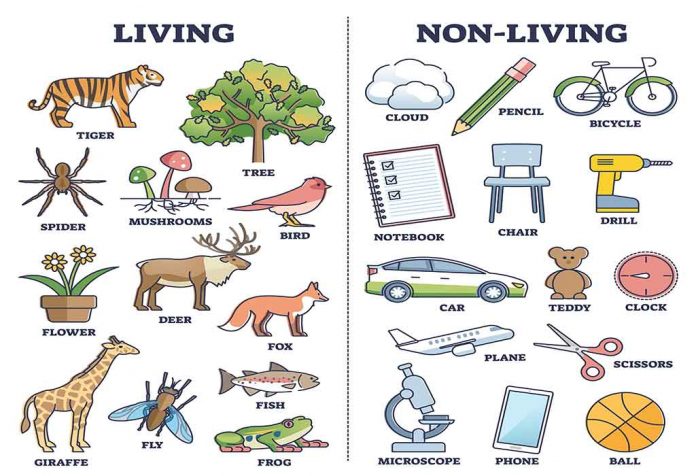
The meaning of living things is simply the things around us that are living – alive and breathing! Anything that has a fixed life cycle is considered to be a living thing.
Some examples of Living things are:
- Animals
- Plants
- Germs
- Fishes
- Birds
- Bacteria
From the examples, can you see a pattern?
All the ‘Living’ things are nothing but organisms that interact with their environment to sustain themselves! Any organism that eats, grows, reproduces and then eventually dies is called a living thing. Natural living things cannot live forever and must eventually perish.
What Are The Characteristics Of Living Things
Teaching living and non-living things to kindergarten students can be tricky. The best way to go about it is to make a checklist of characteristics to which they can compare objects and then decide whether the object is living on non-living.
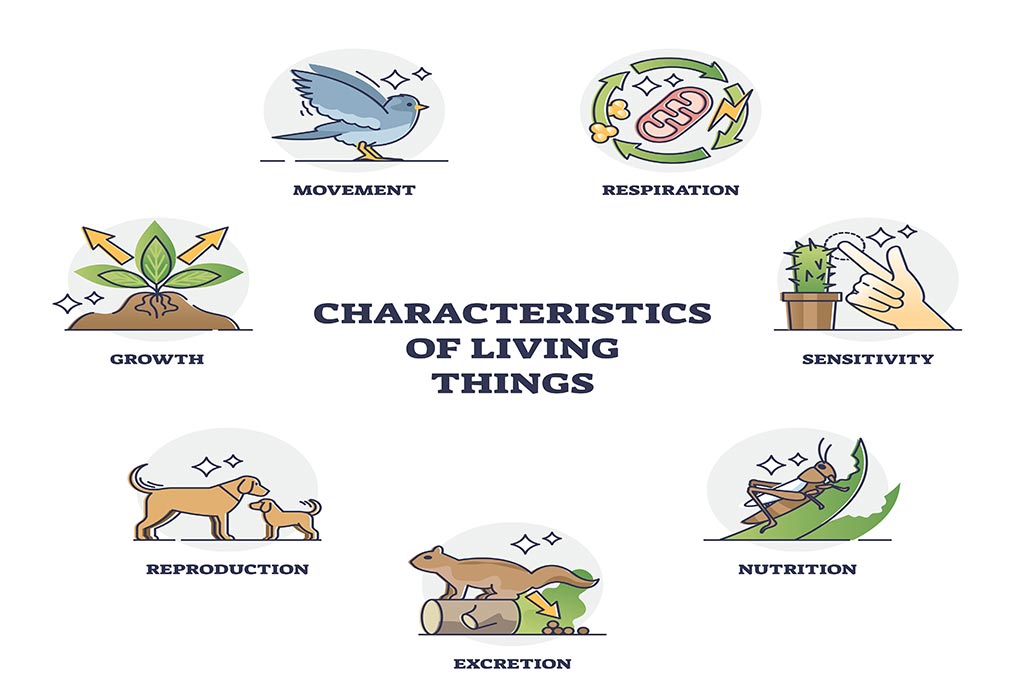
Below are some characteristics of Living things:
1. Organisation
Living things are made up of ‘cells’, which are called the building blocks of life. These ‘cells’ are properly and systematically organised in a living organism. All living beings are made up of one or more cells.
2. Reproduction
A living thing must be able to reproduce. They should be able to create offspring. This can be through both sexual and asexual reproduction. An organism passes on its genetic information to its offspring through reproduction.
3. Growth
All living things grow. We are born a different size, and we die a different size. Other living things, such as plants and fish, grow too!
4. Adjustability
All living things interact and adjust to their environment. We have warm-blooded and cold-blooded organisms; both have unique ways of adjusting their body temperatures according to their environment. Living beings also respond to stimuli in their environment.
5. Require Nutrition
All living organisms require nutrition in some form or another. They require nutrition for growth and survival. For us humans, this means eating food and drinking water, and for plants, this entails making their own food by photosynthesis.
6. Adaptability
All living things must adapt to their environment to have a better chance of survival. One good example of this is how giraffes have really long necks so that they can reach the top of trees where the fresh leaves are situated. Even plants adapt to their environment. One such example is cacti. They are usually found in deserts where water is scarce. Hence, they have developed roots which grow long and deep to be able to find water.
7. Excrete Waste
All living animals excrete waste. As we know, energy can’t be destroyed and is merely passed on from one form to another; excretion is also a form of release of energy from a living organism’s body.
What Are Non-Living Things, And What Are Their Types?
The meaning of non-living things is simply the things around us that are not living. Such objects do not possess life and don’t have a lifespan or need food and energy as living things do. Non-living things merely just exist and share space in the world we call our home.
Non-living things can be characterised as Natural Things and Man Made or Artificial Things.
1. Natural Things
These are things that have formed and existed on their own forever.
Examples
- Rivers
- Oceans
- Mountains
- Hills
- Planets and Stars
2. Man-Made Things
These are objects or items that have been made by humans. Their existence depends on humans.
Examples
- Tables
- Chairs
- Gadgets
- Cars
- Clothes
What Are The Characteristics Of Non-Living Things?
Non-living things, too, have their own characteristics, which help us identify them. Some basic characteristics of non-living things are:
- Non-living things are lifeless objects that do not possess life. They are not made up of living cells and do not perform metabolic activities.
- They cannot travel from one place to another without the help of an external force. Hence, they do not show locomotion.
- They don’t require nutrition. They simply exist without the need for any form of life-supporting processes such as respiration or metabolism.
- They do not reproduce offspring, and there is no process of reproduction involved in their life cycle.
- They do not die. They need to be destroyed using external force or must be consumed for the production of other items.
Difference Between Living Things And Non-Living Things
Below are the differences between living VS nonliving things –
| Living Things |
Non-Living Things
|
| 1. Living things possess life. |
1. They do not possess life.
|
| 2. Made up of living cells which are also called the building blocks of life. |
2. Made up of non-living cells of different materials.
|
| 3. Carry out metabolic activities in their bodies to generate energy. |
3. Don’t generate energy and do not carry out any metabolic activities in their body.
|
| 4. They reproduce to keep the population going. |
4. They do not reproduce.
|
| 5. They are sensitive and respond to stimuli. |
5. They do not respond to stimuli.
|
| 6. Living things respire. |
6. Non-living things do not respire.
|
| 7. Living things age and eventually die from disease or cell death. |
7. Non-living things can’t cease to exist without any external forces destroying them.
|
| 8. They need nutrients and water to survive. |
8. They do not need such things to survive.
|
| 9. Most express emotions and feelings. |
9. They do not have or express emotions.
|
| 10. They show signs of growth from within and often change their shape and size throughout their life. |
10. They do not show signs of any form of growth.
|
FAQs
1. Why are plants classified as living things when they cannot move?
Plants are classified as living things because they are made up of living cells and do show signs of growth. In fact, some plants even move!
2. Why is water a nonliving thing?
Water is considered to be a non-living thing as, on its own, it does not have any life. It is a habitat for other life forms but is not an organism on its own. However, other life forms, such as fish and whales, do call it their home!
3. How do living and nonliving things interact with one another in different habitats?
Living and non-living things interact with each other in every habitat! Air helps birds fly, while the water in the oceans helps aquatic organisms swim and sustain their lives. Us humans constantly interact with natural non-living things for sustenance. Both non-living and living things are equally important!
Also Read:
Teaching Your Child How to Read
Diamond Shape Lesson for Children
Number Names for Children to Improve Their Math Skills