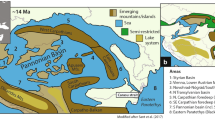
Abstract
Twenty paleogeographic maps are presented for Middle Eocene (Lutetian) to Late Pliocene times according to the stratigraphical data given in the companion paper by Berger et al. this volume. Following a first lacustrine-continental sedimentation during the Middle Eocene, two and locally three Rupelian transgressive events were identified with the first corresponding with the Early Rupelian Middle Pechelbronn beds and the second and third with the Late Rupelian ≪ Serie Grise ≫ (Fischschiefer and equivalents). During the Early Rupelian (Middle Pechelbronn beds), a connection between North Sea and URG is clearly demonstrated, but a general connection between North Sea, URG and Paratethys, via the Alpine sea, is proposed, but not proved, during the late Rupelian. Whereas in the southern URG, a major hiatus spans Early Aquitanian to Pliocene times, Early and Middle Miocene marine, brackish and freshwater facies occur in the northern URG and in the Molasse Basin (OMM, OSM); however, no marine connections between these basins could be demonstrated during this time. After the deposition of the molasse series, a very complex drainage pattern developed during the Late Miocene and Pliocene, with a clear connection to the Bresse Graben during the Piacenzian (Sundgau gravels). During the Late Miocene, Pliocene and Quaternary sedimentation persisted in the northern URG with hardly any interruptions. The present drainage pattern of the Rhine river (from Alpine area to the lower Rhine Embayment) was not established before the Early Pleistocene.




















Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abele G (1977) Morphologie und Entwicklung des Rheinsystems aus der Sicht des Mainzer Raumes. Mainzer geographische Studien 11:245–259 Mainz
Bartz J (1961) Die Entwicklung des Flußnetzes in Südwestdeutschland. Jahreshefte des Geologischen Landesamtes Baden-Würtemberg 4:127–135 Freiburg i. Br
Becker D (2003) Paléoécologie et paléoclimats de la Molasse du Jura (Oligo-Miocène): apport des Rhinoceratoidea (Mammalia) et des minéraux argileux. Thèse Univ Fribourg, Geofocus 9:1–327
Berger JP (1985) La transgression de la Molasse marine supérieure (OMM) en Suisse occidentale. Münchn geowiss Abh A5:1–207
Berger JP (1992) Paléontologie de la Molasse de Suisse occidentale. Thèse d’habilitation Univ Fribourg 25.05.1992, pp 1–450
Berger JP (1995) Des nannofossiles calcaires aux rhinocéros: déplacés au remaniés?. Eclogae geol Helv 88(3):657–680
Berger JP (1996) Cartes paléogéographiques-palinspastiques du bassin molassique Suisse (Oligocène inférieur-Miocène moyen). N Jb Min Geol Pal Abh 202(1):1–44
Berger JP, Reichenbacher B, Becker D, Grimm M, Grimm K, Picot L, Storni A, Pirkenseer C, Schaefer A (2004) Eocene-Pliocene time scale and stratigraphy of the Upper Rhine Graben (URG) and the Swiss Molasse Basin (SMB). Int J Earth Sci, this volume
Boenigk W (1982) Der Einfluß des Rheingraben-Systems auf die Flußgeschichte des Rheins. Zeitschrift für Geomorphologie, Supplementband, vol 42. Stuttgart, Berlin, pp 167–175
Boenigk W (2002) The Pleistocene drainage pattern in the Lower Rhine Basin. In: Rift tectonics and syngenetic sedimentation; the Cenozoic Lower Rhine Basin and related structures. Netherlands J Geosci 81(2):201–209
Bolliger T, Fejfar O, Graf H, Kaelin D (1996) Vorläufige Mitteilung über Funde von pliozänen Kleinsäugern aus den höheren Deckenschottern des Irchels (Kt. Zürich). Eclogae geol Helv 89(3):1043–1048
Dèzes P, Schmid S, Ziegler PA (2004) Evolution of the European Cenozoic Rift System: interaction of the Alpine and Tyrenean orogens with their foreland lithosphere. Tectonophysics (in press)
Diem B (1986) Die Untere Meeresmolasse zwischen der Saane und Ammer. Eclogae geol Helv 79(2):493–559
Giamboni M, Ustaszewski K, Schmid SM, Schumacher ME, Wetzel A (2004) Plio-Pleistocene transpressional reactivation of paleozoic and paleogene structures in the Rhine-Bresse transform zone (northern Switzerland and eastern France). Int J Earth Sci (accepted)
Graf HR (2003) Geschichte des unteren Thurtales. Mitt der Thurgauischen Naturforsch Ges 59:7–30
Heumann G, Litt T (2002) Stratigraphy and paleoecology of the Late Pliocene and Early Pleistocene in the open-cast mine Hambach (Lower Rhine basin). In: Schaefer A, Siehl A (eds) Rift tectonics and syngenetic sedimentation; the Cenozoic Lower Rhine Basin and related structures. Geologie en Mijnbouw. Neth J Geosci 81(2):193–199
Kälin D, Weidmann M, Engesser B, Berger J-P (2001) Paléontologie et âge de la Molasse d’eau douce supérieure (OSM) du Jura neuchâtelois. Mémoires suisses de paléontologie 121:65–99
Kuhlemann A, Kempf O (2002) Post-eocene evolution of the North Alpine Foreland Basin and its response to Alpine tectonics. Sediment Geol 152:45–78
Kuhlemann J, Spiegel C, Dunkl I, Frisch W (1999) A contribution to the middle Oligocene paleogeography of Central Europe: new evidence from fission tracks ages of the Southern Rhine graben. N Jb Geol Palaeontol Abh 214:415–432
Liniger H (1966) Das plio-altpleistozäne Flussnetz der Nordschweiz. Regio Bas 7(2):158–177
Müller WH, Naef H, Graf HR (2002) Geologische Entwicklung der Nordschweiz, Neotektonik und Langzeitszenarien Zürcher Weinland. NAGRA technischer bericht 99–08, p 237
Petit C, Campy M, Chaline J, Bonvalot J (1996) Major paleogeographic changes in Alpine Foreland during the Pliocene—Pleistocene. Boreas 25:131–143
Picot L (2002) Le Paléogène des synclinaux du Jura et de la bordure sud-rhénane: paléontologie (Ostracodes), paléoécologie, biostratigraphie et paléogéographie. Thèse Univ Fribourg, Geofocus 5, pp 1–240
Picot L, Becker D, Lapaire F, Ustaszewski K, Hug WA, Berger JP (2004) Sédimentologie, paléontologie et paléoenvironnements côtiers de la région de Porrentruy (sud - rhénan): implications géodynamique. Eclogae geol Helv (accepted)
Reichenbacher B (2000) Das brackish-lakustrine Oligozän und UnterMiozän im Mainzer Becken und Hanauer Becken: Fischfaunen, Paläoökologie, Biostratigraphie, Paläogeographie. Cour Forschung Senckenberg 222:1–143
Reichenbacher B, Böttcher R, Bracher H, Doppler G, von Engelhardt W, Gregor HJ, Heissig K, Heizmann EPJ, Hofmann F, Kälin D, Lemcke K, Luterbacher H, Martini E, Pfeil F, Reiff W, Schreiner A, Steininger FF (1998) Graupensandrinne—Ries-Impakt: Zur Stratigraphie der Grimmelfinger Schichten, Kirchberger Schichten und Oberen Süsswassermolasse (nördliche Vorlandmolasse, Süddeutschland). Z dt geol Ges 149(1):127–161
Roll A (1979) Versuche einer Volumenbilanz der Oberhreingrabens und seiner Schultern. Geol Jb Riehe A, vol 52. p 82
Schlunegger F, Pfiffner A (2001) The sedimentary response of the North Alpine Foreland basin to changes in erosional processes in the Alps. IAS 2001, 21st Meeting, Davos, 3–5 September 2001. Excursion guides, pp 85–99
Schlunegger F, Slingerland R, Matter A (1998) Crustal thickening and crustal extension as controls on the evolution of the drainage network of the central Swiss Alps between 30 Ma and the present: constraints from the stratigraphy of the North Alpine Foreland Basin and the structural evolution of the Alps. Basin Res 10(2):197–212
Semmel A (1983) Die plio-pleistozänen Deckschichten im Steinbruch Mainz-Weisenau—Geologisches Jahrbuch Hessen 111:219–233 Wiesbaden
Sissingh W (1998) Comparative Tertiary stratigraphy of the Rhine graben, Bresse graben and Molasse basin: correlation of Alpine foreland events. Tectonophysics 300:249–284
Sissingh W (2003) Tertiary paleogeographic and tectonostratigraphic evolution of the Rhenish Triple Junction. Paleogeogr Paleoclimatol Paleoecol 196:229–263
Acknowledgements
We thank D. Kälin (Bern), M. Hottenrott and G. Radtke (Wiesbaden), T. Griessemer (Mainz), M. Lutz (Freiburg im Br.), W. Sissingh (Utrecht) for stimulating discussion. We are grateful to P.A. Ziegler (Basel) and J. Kuhleman (Tübingen) for their comments, which helped improve this paper. Financial support by the Swiss National Science Foundation, projects 21.52359.97, 20.59220.99 & 20–66935.01, as well as by the EUCOR-URGENT-Project, is gratefully acknowledged.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Berger, JP., Reichenbacher, B., Becker, D. et al. Paleogeography of the Upper Rhine Graben (URG) and the Swiss Molasse Basin (SMB) from Eocene to Pliocene. Int J Earth Sci (Geol Rundsch) 94, 697–710 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-005-0475-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00531-005-0475-2